The Major Symptoms of Arrhythmia and What You Need to Know

Welcome to Bay Regional Medical Center's comprehensive guide on understanding and addressing the major symptoms of arrhythmia. As a leading healthcare provider in the field of cardiology and cardiovascular care, we aim to equip you with the knowledge necessary to identify these symptoms and seek appropriate medical attention promptly.
What is Arrhythmia?
Arrhythmia refers to an abnormal heart rhythm that can have various underlying causes. It occurs when the electrical signals that regulate the heart's beating pattern become disrupted. This disruption can affect the heart's ability to pump blood effectively, potentially leading to complications and other health issues. Identifying the symptoms of arrhythmia promptly is crucial in managing the condition.
Common Symptoms of Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia can manifest in diverse ways, and recognizing its symptoms can aid in early detection and treatment. Here are some of the major symptoms associated with arrhythmia:
- Palpitations: A notable awareness of your heartbeats, often described as rapid, irregular, or fluttering.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness: Feeling faint or unsteady, which may occur during or right after an arrhythmia episode.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty catching your breath, particularly during physical activity or rest.
- Chest pain: Discomfort, pressure, or a squeezing sensation in the chest region.
- Fatigue: Generalized exhaustion or tiredness, even after minimal exertion or restful periods.
- Fainting spells: Losing consciousness or passing out, often for a short duration.
- Weakness: A sense of weakness or decreased strength in the body.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of the aforementioned symptoms or suspect you may have arrhythmia, it is important to consult a healthcare professional, preferably a cardiologist, for further evaluation and guidance. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment can significantly improve your quality of life and reduce the risk of complications associated with arrhythmia.
Diagnosing Arrhythmia
Diagnosing arrhythmia involves a comprehensive evaluation that may include the following:
- Medical history: Your healthcare provider will inquire about your symptoms, medical history, and any medications you are currently taking.
- Physical examination: A thorough physical examination will be conducted, including listening to your heartbeat and checking for any signs of underlying health issues.
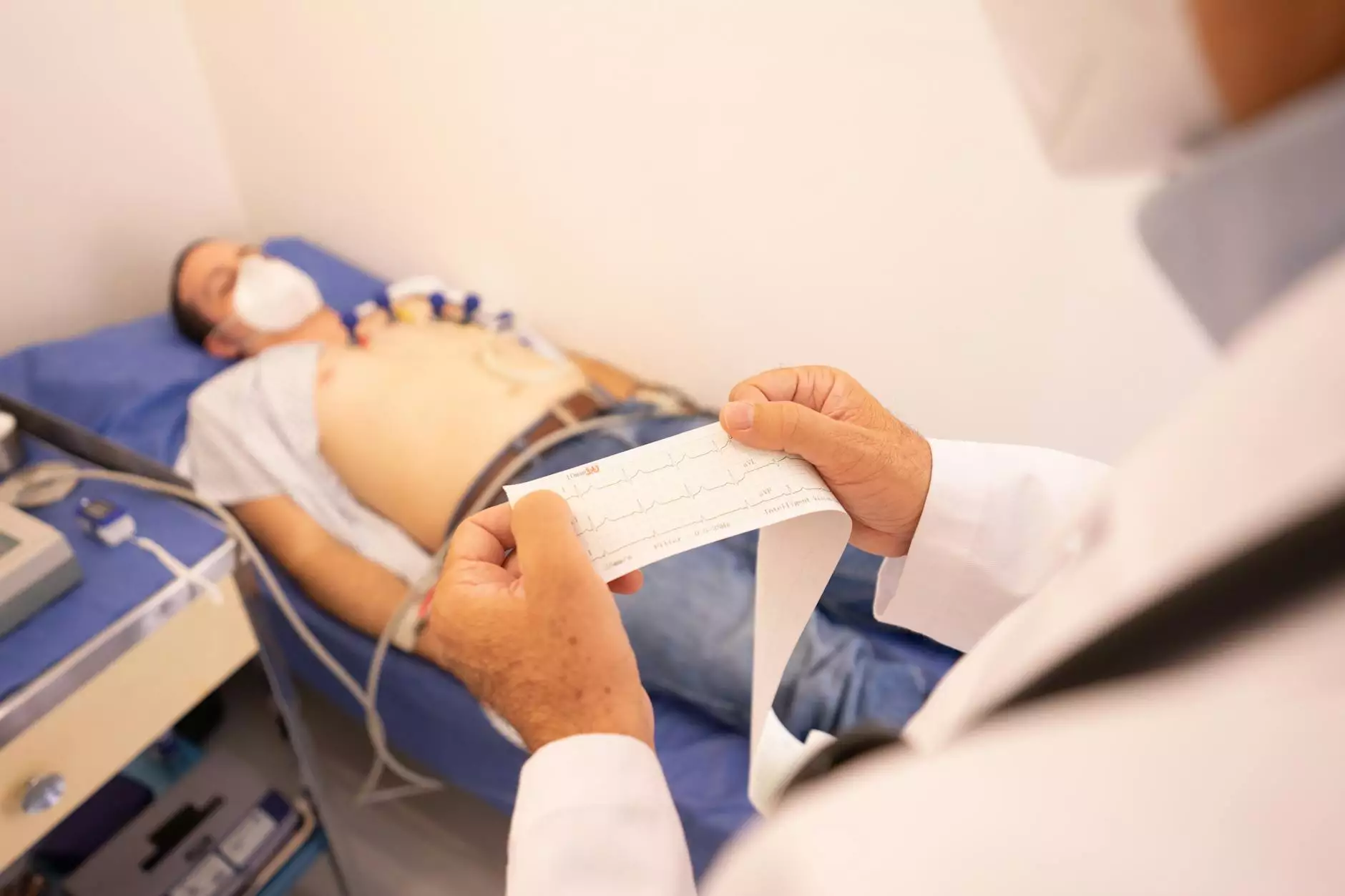
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): This non-invasive test records the electrical activity of your heart, providing valuable insights into its rhythm and any abnormalities present.
- Holter monitor: A portable device that tracks your heart's electrical activity continuously over a 24 to 48-hour period, allowing for the identification of arrhythmia episodes that may not occur during a regular ECG.
- Echocardiogram: This imaging test utilizes sound waves to create detailed images of the heart's structure and function, aiding in visualizing any irregularities.
- Stress test: This evaluation involves monitoring your heart's response to physical exertion, helping to identify stress-induced arrhythmias.
Treatment Options
A personalized treatment plan will be developed based on your specific condition, medical history, and individual needs. Treatment options for arrhythmia may include:
- Medications: Prescription medications can help regulate your heart rhythm and manage underlying conditions contributing to arrhythmia.
- Cardioversion: This procedure involves the use of electric shocks or medications to restore a normal heart rhythm.
- Catheter ablation: A minimally invasive procedure where a catheter is guided to the heart to correct the source of the arrhythmia through controlled energy delivery.
- Implantable devices: Devices like pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) can help monitor and regulate your heart's rhythm effectively.
- Open-heart surgery: In certain cases, surgery may be required to treat complex arrhythmias or address underlying heart conditions contributing to the rhythm disturbances.
Living with Arrhythmia
While managing arrhythmia requires medical intervention, lifestyle changes are also crucial for living a healthy and fulfilling life. Here are some practical tips to consider:
- Eat a balanced diet: Opt for heart-healthy foods rich in essential nutrients and limit the consumption of processed and high-sodium foods.
- Engage in regular exercise: Consult your healthcare provider to determine an exercise regimen that suits your health condition, as physical activity can contribute positively to heart health.
- Manage stress levels: Incorporate stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and engaging in activities you enjoy.
- Avoid tobacco and excessive alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can have detrimental effects on your heart and overall health.
- Follow your treatment plan: It is essential to strictly adhere to your prescribed medications, therapies, and recommended follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Bay Regional Medical Center extends its commitment to providing comprehensive information regarding the major symptoms of arrhythmia and the steps necessary for proper diagnosis and management. By understanding the symptoms, seeking timely medical attention, and following appropriate treatment plans, individuals can lead fulfilling lives despite having arrhythmia. It is our hope that this guide has empowered you to take the necessary steps towards prioritizing your heart health and overall well-being.