The Importance of Grain Drying: A Comprehensive Guide

In the agricultural sector, grain drying stands as a pivotal process that directly impacts the quality, viability, and profitability of crops. With increasing global demand for food and the perils of climate change, understanding the importance of grain drying has never been more critical. This article delves into the significance, methods, challenges, and future prospects of grain drying, aiming to equip farmers, agronomists, and stakeholders with essential knowledge that can enhance productivity and sustainability.
Why is Grain Drying Essential?
The core reason for grain drying is to reduce the moisture content of harvested grains. Excess moisture can lead to a plethora of problems, including spoilage, the growth of molds, and infestations by pests. Below, we explore the key reasons why grain drying is vital:
1. Preservation of Grain Quality
Grains harvested with high moisture content are at risk of quality degradation. Proper drying helps to maintain:
- Flavor: Correct moisture levels are crucial in preserving the flavor profile of grains.
- Texture: Grains that are too moist can become mushy and lose their texture.
- Color: Drying retains the natural coloration of grains, enhancing visual appeal.
2. Prevention of Spoilage and Disease
High moisture content is a breeding ground for bacteria, fungi, and pests. Effective drying significantly lowers the risk of:
- Mold Growth: Mold can produce mycotoxins which are toxic and harmful to health.
- Insect Infestation: Dry conditions deter pests that can devastate grain reserves.
3. Improved Storage and Handling
Well-dried grains are easier to store and handle. Key benefits include:
- Extended Shelf Life: Low moisture content promotes longevity in storage.
- Reduced Weight: Drier grains weigh less, which can save on transportation costs.
Methods of Grain Drying
There are several methods available for drying grain, each with its pros and cons. Understanding these methods is vital for selecting the best approach tailored for specific grain types and conditions.
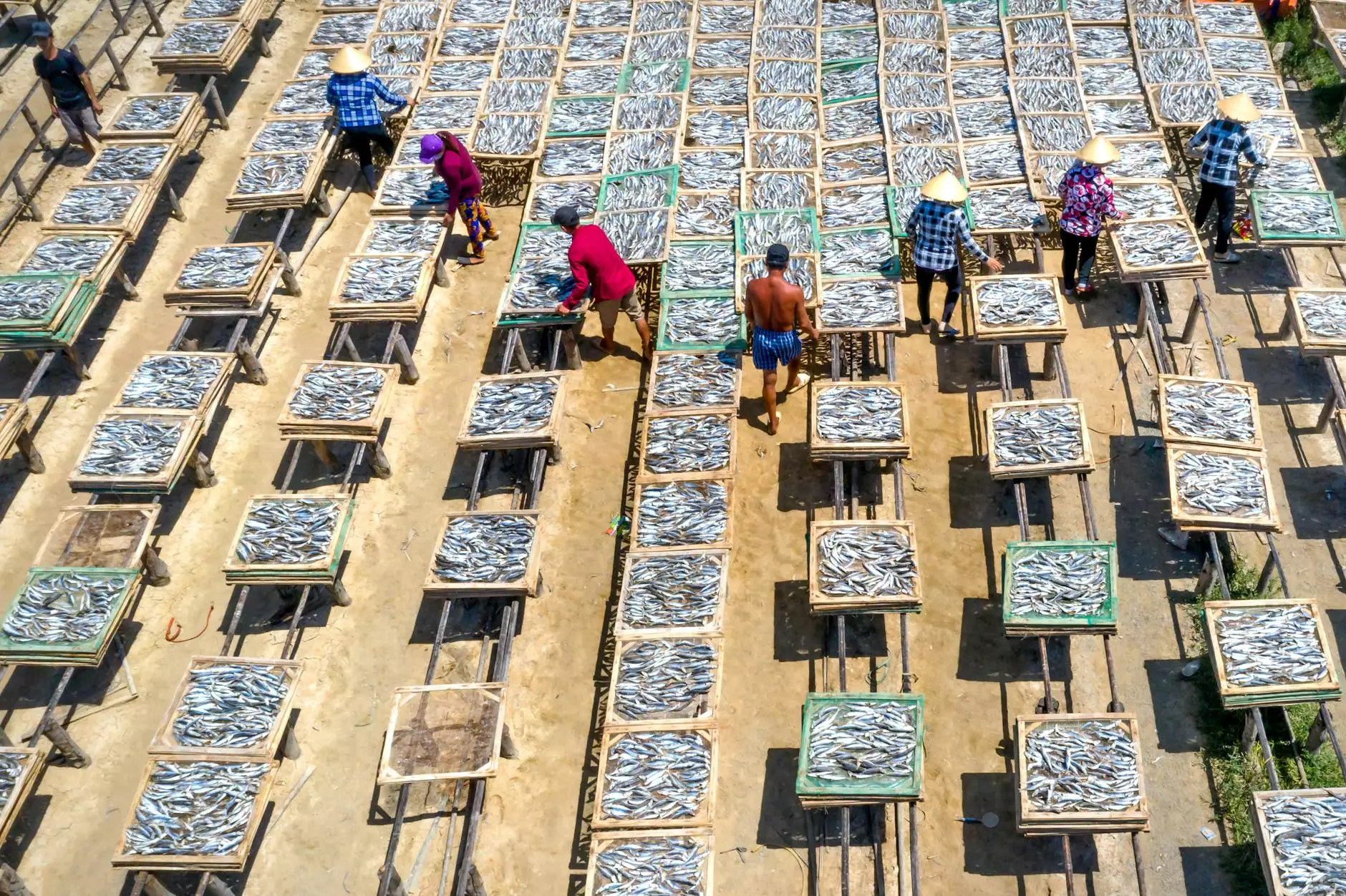
1. Natural Drying
Natural drying, often termed sun drying, involves spreading grains in thin layers under the sun. Although this method is the most cost-effective, it is highly dependent on weather conditions and requires ample time. Additionally:
- Advantages: No energy costs and minimal equipment.
- Disadvantages: Risk of contamination, uneven drying, and prolonged exposure to weather issues.
2. Mechanical Drying
Mechanical drying utilizes specialized equipment, such as grain dryers, which provide controlled conditions for drying. These options include:
- Continuous Flow Dryers: Ideal for large farms; they allow ongoing drying, facilitating smooth operations.
- Batch Dryers: Suitable for smaller operations; they require loading and unloading, hence are less efficient in time management.
- Bin Dryers: They can be used with hot air or heated air to evaporate moisture effectively.
3. Hybrid Drying Systems
Combining both natural and mechanical methods, hybrid drying systems provide the best of both worlds—efficient energy usage balanced with reduced operational costs.
Challenges in Grain Drying
While the process of grain drying is crucial, it is not without challenges. Effective grain drying must contend with numerous hurdles that can affect both quality and efficiency. Some of these include:
1. Moisture Measurement
Accurate moisture measurement is essential for effective drying. Failure to gauge moisture content can lead to:
- Under-drying: This results in spoilage during storage.
- Over-drying: Decreased weight and potential damage to the grain itself.
2. Energy Consumption
Mechanical dryers can be energy-intensive, leading to high operational costs. Farmers need to consider:
- Cost of Fuel: Fossil fuels and electricity can significantly impact profits.
- Renewable Energy Options: Leveraging solar or wind energy can help mitigate costs.
3. Weather Dependency
Natural drying methods hinge on favorable weather conditions, which can lead to:
- Inconsistent results: Variations in moisture levels depending on the drying day.
- Extended Harvest Times: Delaying storage and potentially risking crop damage.
Future Perspectives on Grain Drying
As the agricultural industry evolves, so too does the technology and methods involved in grain drying. Innovations are paving the way for more efficient and sustainable practices. Some promising advancements include:
1. Smart Drying Technologies
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology can provide real-time monitoring and precise control of grain drying processes. These systems can streamline:
- Temperature Control: Ensuring optimal drying without damaging the crop.
- Data Analytics: Allowing farmers to analyze factors affecting drying and adjust practices accordingly.
2. Renewable Energy Utilization
With growing concerns regarding climate change, sustainable drying methods using renewable resources are on the rise. Innovative options include:
- Solar Drying: Harnessing the sun's energy to power dryers.
- Biomass Drying: Utilizing agricultural waste as a fuel source.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of Grain Drying
The importance of grain drying cannot be overstated. It is a fundamental practice that ensures the quality of grains, prolongs their storage life, and enhances profitability for farmers. As methods evolve with technology, the future of grain drying is set to become even more efficient and sustainable, proving that it is not just a necessary practice but a pillar of modern agriculture. By understanding and implementing effective grain drying techniques, stakeholders can adapt to challenges and position themselves for long-term success in the highly competitive agricultural marketplace.